Explain Basic 2D (2 Dimensional) Translation in OPENGL with example and output in OPENGL.
Computer Graphics and VisualizationExplanation
Translation
-
A translation moves all points in an object along the same straight -line path to new positions .
-
The path is represented by a vector, called the translation or shift vector.
-
We can write the components:
p'x = px + tx
p'y = py + ty -
or in matrix form:
P' = P + T
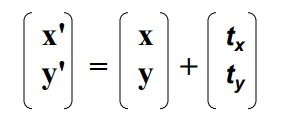
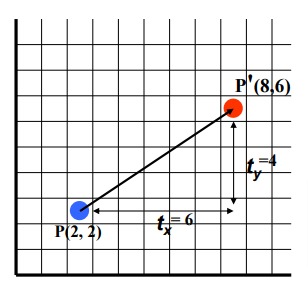
Example:-
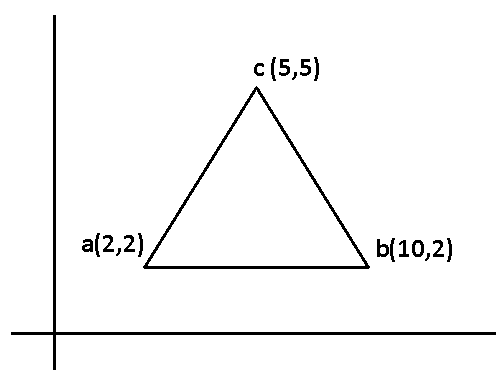
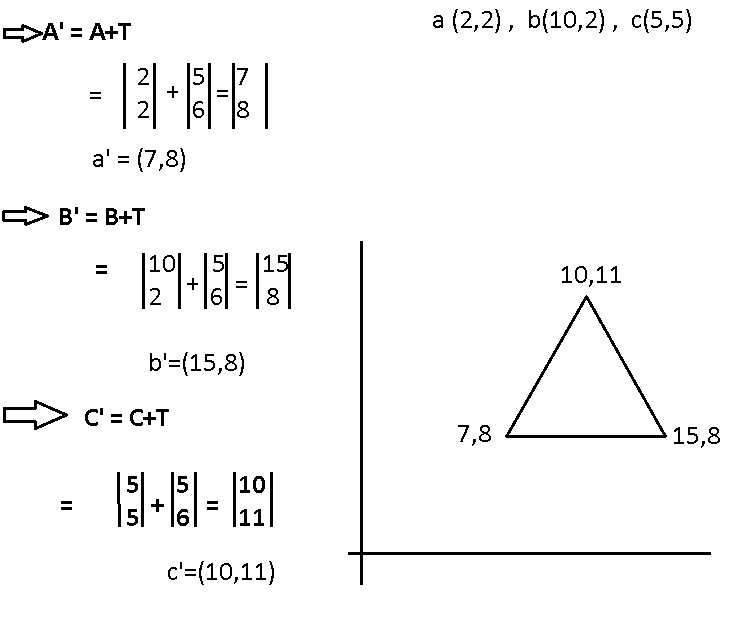
A(2,2), F(10,2), C(5,5), Translate the triangle with dx=5 , dy=6
⇒ P1=P+T
Code For OPENGL :-
/* c program for 2d translation */
#include<stdio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
int gd=DETECT,gm;
int n,xs[100],ys[100],i,ty,tx;
void draw();
void translate();
void main()
{
printf("Enter number of sides of polygon: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter co-rdinates: x,y for each vertex );
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&xs[i],&ys[i]);
printf ("Enter distances for translation (in x and y directions): ");
scanf("%d%d",&tx,&ty);
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "C:\\TURBOC3\\BGI\\");
cleardevice();
//drawing original polygon in RED color
setcolor (RED);
draw();
//Doing translation
translate();
//drawing translated polygon in YELLOW color
setcolor(YELLOW);
draw();
getch();
}
void draw()
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
line(xs[i],ys[i],xs[(i+1)%n],ys[(i+1)%n]);
}
void translate()
{
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
xs[i]+=tx;
ys[i]+=ty;
}
}
Output :
