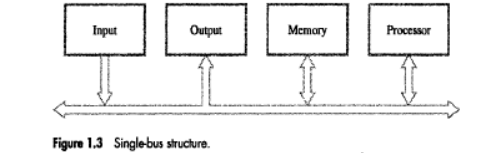
Single bus structure.
COMPUTER ORGANIZATIONExplanation
BUS STRUCTURE -
• A bus is a group of lines that serves as a connecting path for several devices.
• Bus must have lines for data transfer, address & control purposes.
• Because the bus can be used for only one transfer at a time, only 2 units can actively use the bus at any given time.
• Bus control lines are used to arbitrate multiple requests for use of the bus.
• Main advantage of single bus: Low cost and flexibility for attaching peripheral devices.
• Systems that contain multiple buses achieve more concurrency in operations by allowing 2 or more transfers to be carried out at the same time. Advantage: better performance. Disadvantage: increased cost.
• The devices connected to a bus vary widely in their speed of operation. To synchronize their operational speed, the approach is to include buffer registers with the devices to hold the information during transfers. Buffer registers prevent a high-speed processor from being locked to a slow I/O device during a sequence of data transfers.