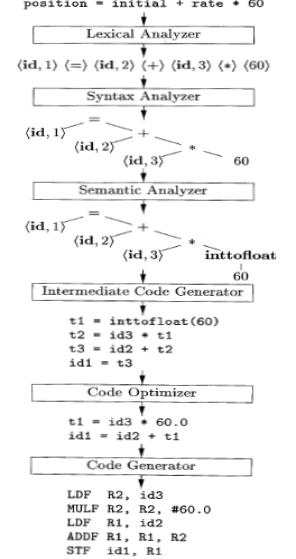
Explain with a neat diagram phases of a compiler by taking an example A=B+C*60.
Solution
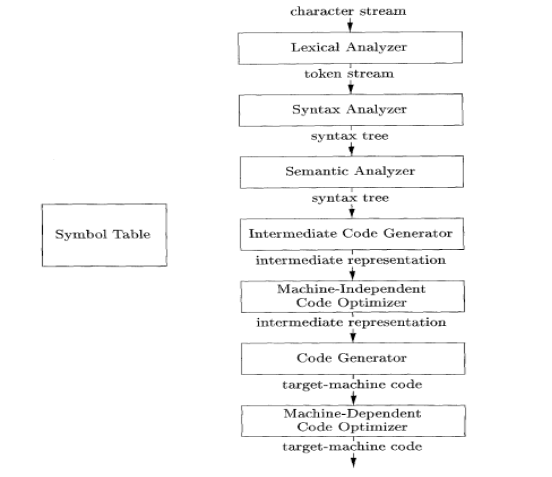
1) Lexical Analyzer
— The first phase of compiler is lexical analyzer it reads stream of characters in the source program
— Groups the characters into meaningful sequences – lexemes
— For each lexeme, a token is produced as output
— <token-name , attribute-value>
Token-name : symbol used during syntax analysis
Attribute-value : an entry in the symbol table for this token
— Information from symbol table is needed for syntax analysis and code generation
— Consider the following assignment statement
2) Syntax Analysis
The second phase of compiler is syntax analysis is also called Parsing
— Parser uses the tokens to create a tree-like intermediate representation
— Depicts the grammatical structure of the token stream
— Syntax tree is one such representation
Interior node – operation
Children - arguments of the operation
Other phases use this syntax tree to help analyze source program and generate target program
3) Semantic Analysis
The third phase of compiler is Semantic Analyzer
— Checks semantic consistency with language using:
Syntax tree and Information in symbol table
— Gathers type information and save in syntax tree or symbol table
— Type Checks each operator for matching operands
Ex: Report error if floating point number is used as index of an array
— Coercions or type conversions
Binary arithmetic operator applied to a pair of integers or floating point numbers
If applied to floating point and integer, compiler may convert integer to floating-
point number
4) Intermediate Code Generation
After syntax and semantic analysis Intermediate Code Generation is the fourth phase of compiler
— Compilers generate machine-like intermediate representation
— This intermediate representation should have the two properties:
Should be easy to produce
Should be easy to translate into target machine
Three-address code
— Sequence of assembly-like instructions with three operands per instruction
— Each operand acts like a register
Points to be noted about three-address instructions are:
— Each assignment instruction has at most one operator on the right side
— Compiler must generate a temporary name to hold the value computed by a three-address instruction
— Some instructions have fewer than three operands
5) Code Optimization
Attempt to improve the target code
— Faster code, shorter code or target code that consumes less power
Optimizer can deduce that
— Conversion of 60 from int to float can be done once at compile time
— So, the inttofloat can be eliminated by replacing 60 with 60.0
— t3 is used only once to transmit its value to id1
6) Code Generation
— Takes intermediate representation as input
— Maps it into target language
— If target language is machine code
Registers or memory locations are selected for each of the variables used
Intermediate instructions are translated into sequences of machine instructions
performing the same task
— Assignment of registers to hold variables is a crucial aspect